System Calls
Compilation Process
Whenever an userspace application wants to interact with kernel, then it has to go via the system call process. So the program with a simple fork or open calls will interact with C methods.
Native code means a code that's compiled to run a specific OS and CPU instruction set. This is mostly the machine language implemented using the CPU'S instruction set.
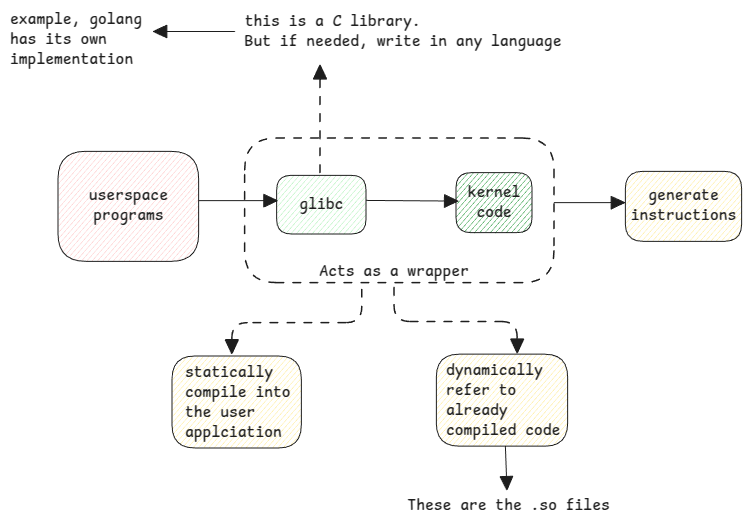
Linux is written in C and so the kernel developers also deliver userspace C libraries called glibc to interact with the kernel.
So when writing C programs, these libraries can be used by other user applications to do system calls to kernel.
Consider the methods in these libraries as wrappers to the actual native functions.
Execution Process
Execution of a system calls involves setting up of CPU registers with the ID of the system call handler method which will then be used by the kernel interrupt handler.
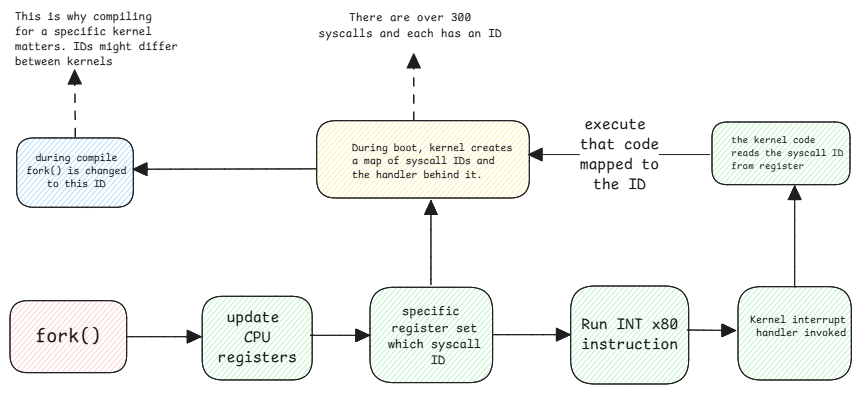
System Call Flow
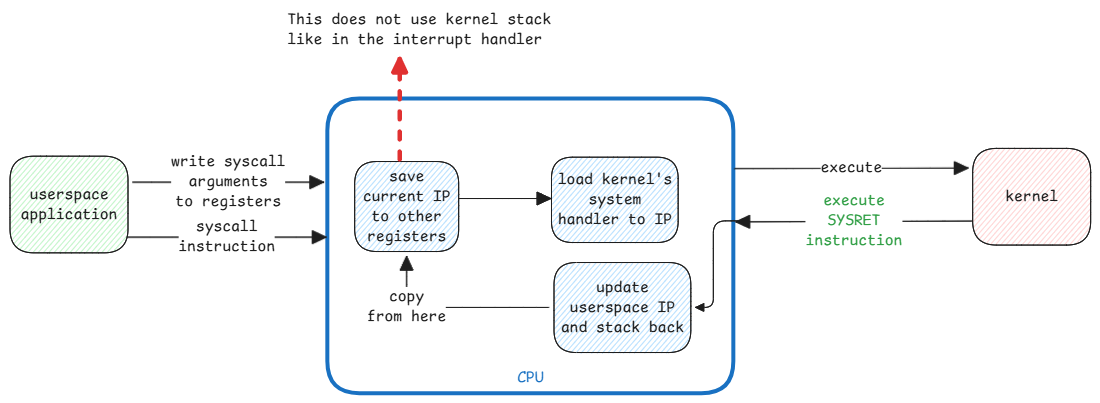
The most important part of system calls is the context switching back from kernel space to userspace.
The kernel executes the SYSRET instruction to switch back to userspace. When this is executed, the CPU switches the kernel's ring mode and also updates the IP, stack pointer and the page tables to point to userspace process.