Bitcoin
Bitcoin is the first cryptocurrency and the most popular one. At the same time the underlying bitcoin network is also open sourced and can be used to build other solutions such as SSI.
It's also the first practical implementation of blockchain technology.
How mining works?
Miners are special nodes because these are the ones with high computational needs. They're in the network and get the list of transactions that are yet to be added to the blockchain.
They run compute intensive hashing task to generate an hash of the block header. It's important that the variable is the nonce value which is constantly changed until the hash value is less than the target hash value. Here the puzzle is to find the nonce value.
nonce means number used once.
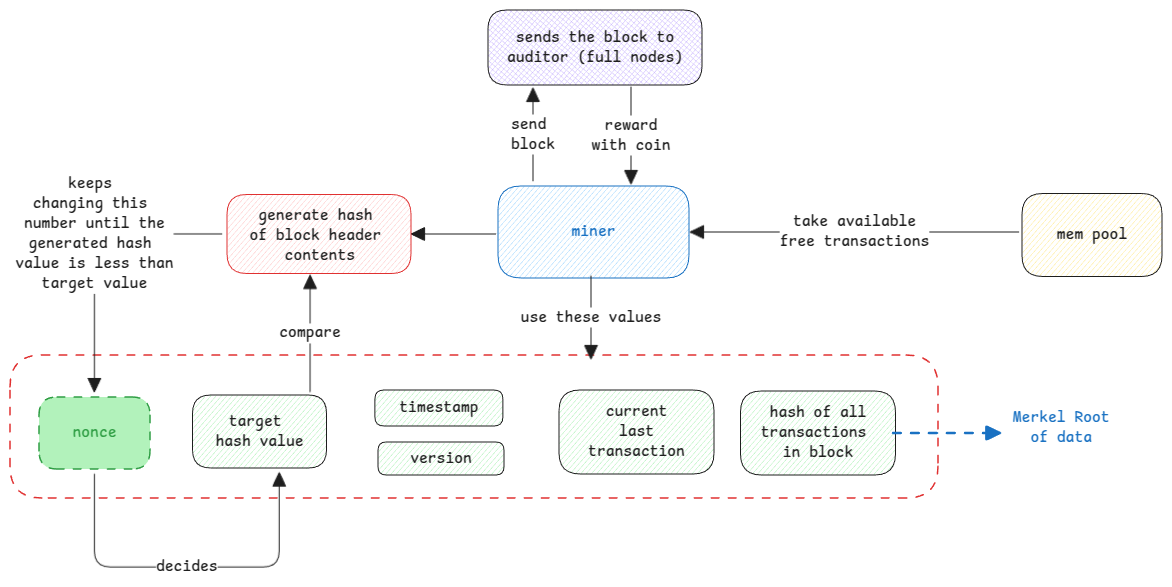
The protocol is built in a way to ensure the mining of a block takes 10 minutes always. This basically means, the target hash value is adjusted such that the mining takes always the same amount of time.
Bitcoin Rewards
The bitcoin is rewarded to miners for the work they do to generate blocks. It's then up to the miners to transfer or sell it to anybody else. This is how new bitcoins first come to the network.
coinbase is the term given to the reward transaction done. This is added as a transaction in the generated block to claim the reward.
Comparing cryptocurrency with normal currency isn't the right one. It's better to compare it with gold. Both gold and cryptocurrency are mined (only when miners generate a block, new bitcoins are released) and both are limited in availability.
Transaction Fees
In addition to the mining reward, the miner also gets transaction fees. This fees depends on the transactions that are part of the block. When a transaction is initiated by the user, the wallet software automatically sets this value depending on many factors.
The transaction fees is also paid in bitcoins.
Miners pick transactions
It's left to the miners to pick transactions in the block based on the transaction fees offered by the user or any other condition. So this means, each miner can be mining any transaction that it can pick from the mempool.
If two miners have generated a block at same time and in case both have any transaction common,
- Some of the peer nodes will receive first generated block and it will accept it and to blockchain.
- Some of the peer nodes will receive second generated block and it will accept it and to blockchain.
- Now a temporary fork occurs. This means, two versions of the blockchain exists in the network.
- Now the miner which builds the third block will add to whatever blockchain it receives from it's full node.
- So this blockchain now becomes the longest one becomes the active one and other blockchain is discarded.
Gossip Protocol
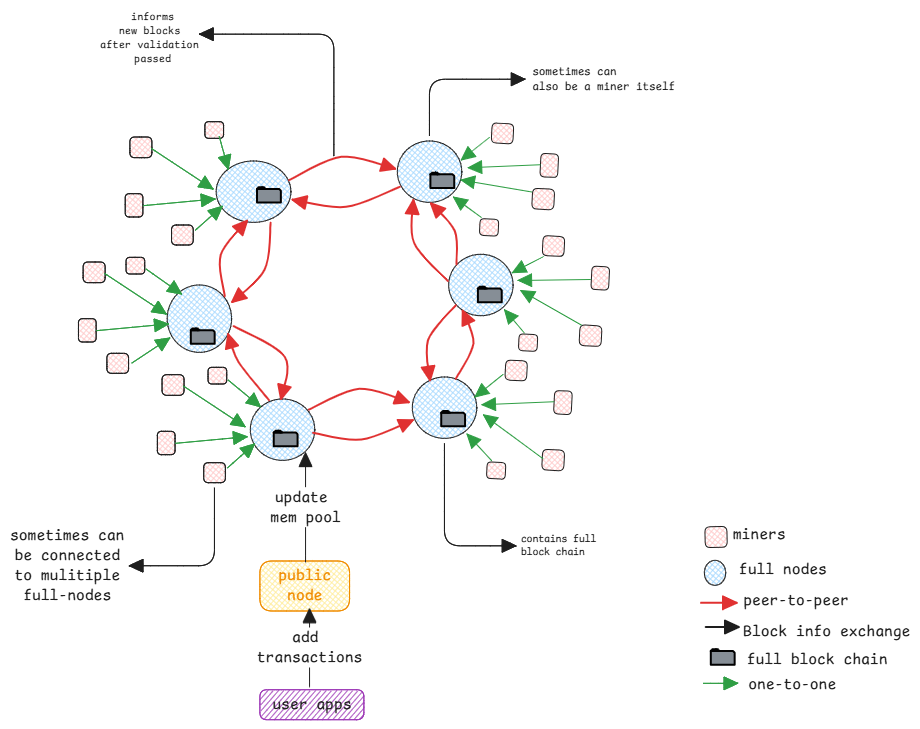
The peer-to-peer communication between the blockchain nodes is done using gossip protocol. In this protocol, the peer broadcasts the information to all connected nodes and the connected nodes forward to the next connected nodes.
Here not all nodes are connect to all other nodes in the network. There is a limit on number of nodes a node in the network connects to.
Software in nodes and miners
Nodes and miner servers are hosting application in any programming language and communicate with other nodes using TCP.
It's important to understand that the bitcoin network is just another software. The term sounds complex but it's just a different way of implementing a distributed system.
Network Setup
How errors are handled?
Assume a block was validated and accepted by one full node and forwarded it to its peers. Now if a peer rejects it, then there is a temporary fork in the network.
Now the miners connected to this node which accepted the block will continue to build on this block. The miners which are working connected to other nodes which start building on the correct last updated block.
Eventually, the blockchain with more blocks will be accepted by the network and the other blockchain will be discarded.
Digital Signatures
The user signs the transaction using their private key. The node which receives the transaction will verify the signature using the public key. This is done using digital signatures.
Final Balance
The transactions are spread across multiple blocks. So in case of an bank account, the final balance of an user isn't stored anywhere. It must be calculated from the entire history of transactions.
Even though the history is in the full chain, the frameworks implement a different caching or calculating mechanism, where the final balances are also calculated and stored in the separate place and the address of this information is linked in the block headers.