Class Proxies
We come across proxy objects while working with Spring framework. It's interesting to see what are these proxy objects and how are the classes of these proxy objects created at runtime.
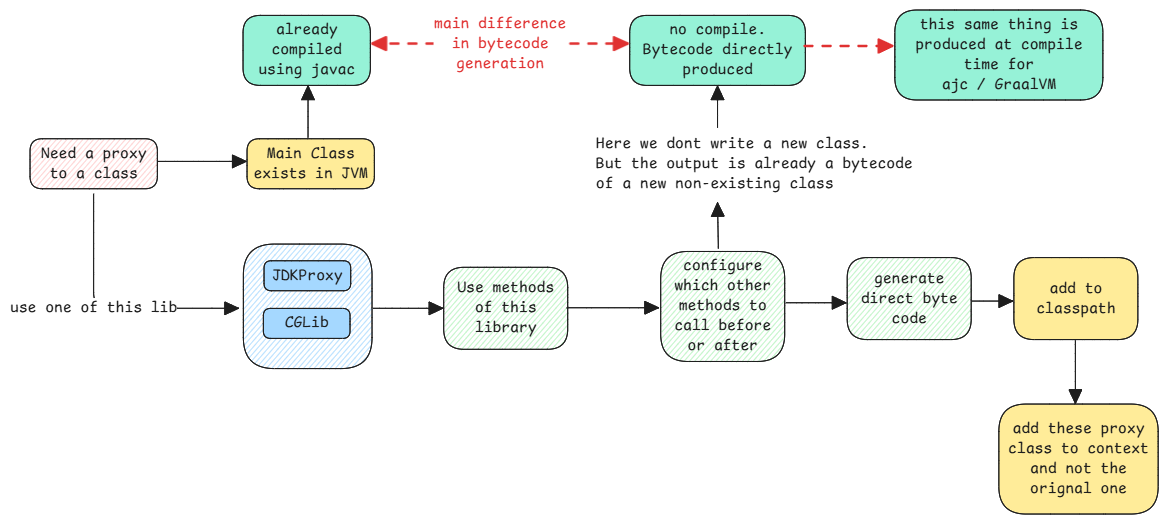
The important point to keep here in mind is the fact that the proxy classes are directly generated by JVM at runtime. Not as standard .java files but directly as .class files in memory and added to classpath.
Implement Interfaces
When a class implements a specific interface then proxies for such classes are generated using JDK Proxy library. Here the library creates a proxy class which also implements the same interface. The implementing method does additional stuff before and after calling the original object's interface implementation.
Spring ensures that only the proxy class is registered as an implementation of the interface to the application context.
Super class
When a class doesn't implement any interface then proxies for such classes are generated using CGLIB library. Here the library creates a child class of the target class and then overrides the methods. Finally the calls the super.method() to call the target class's code as well.
When a bean is instantiated, Spring triggers the post bean processing. As part of that, the proxies are created and the only the proxy bean is registered to the application context.
In case of Spring or other similar frameworks, it handles the logic to ensure only the generated proxy classes are returned when requested.
If we write plain Java code, then it's the responsibility of the code to check and use the proxy classes.