JPA Transactions
In Spring, when we use @Transactional annotation on any method, then the framework will start a session at the beginning of the method which is annotated and then commit all transactions in the entire thread when the method returns.
If there are multiple @Transactional annotated methods in the flow, then share the same transaction (the outermost) unless otherwise specified.
For methods without don't have a dedicated annotation
- If calls are done via spring-data CrudRepository, these methods already have this annotation. So the transaction is handled at that level.
- If direct calls are done, then every single query is handled as a separate transaction, executed and committed individually.
Thread Safe Components
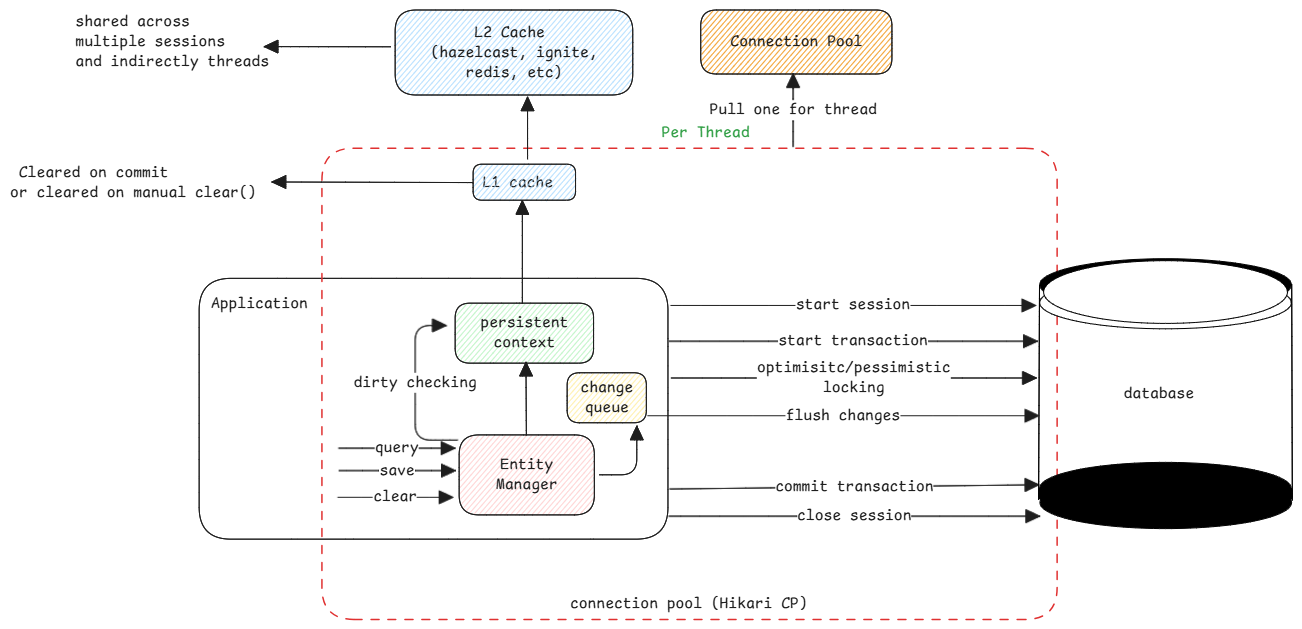
The following components are thread-safe in a JPA transaction
- Entity Manager - All interactions to the database and persistent context happens through this.
- Persistent Context - Consider this as a map of DB entities known to the thread. This is also called the L1 cache.
Shared Components
The following components are shared across threads
- L2 Cache - Systems that can share DB entities across multiple threads. For example, Hibernate clears the cache entry if an entity is updated.
- Connection Pool - The connections to the database are created and shared between threads.
The connection pool threads ensures the connection to the DB is kept alive always.
It's nothing but connection to the database URL, provide credentials and keep ready to start a session.
It uses TCP keep-alive to ensure the connection remains active as long as the connection pool is active.
Proxy Classes
Spring framework doesn't weave connection start and end code into the actual classes. Instead if a class has a transactional annotation, then a proxy class (and it's bean) is created which are then used by the calling application.
This proxy bean then first starts the transaction and then calls the real bean.
If a class is directly instantiated and called then the proxy class isn't used and thereby the transaction isn't managed.
Locking
Database locking features is implemented by JPA and hibernate.
Read more about it here.