Memory-Mapped IO
MMIO is a technique where all IO devices are accessed using the same way how memory is accessed. Memory is accessed using it's address pointers. Similarly, in MMIO the address registers of the devices are added as regular address in the CPU's known list of addresses.
It provides an unified and standard way of accessing all IO devices. This means, device drivers, OS can all access everything in the same way.
Address mapping
At boot, the kernel queries all connected devices and its information. After that the devices are initialized and assigned memory in the same address space which the CPU uses to access memory.
This means, the page table of the kernel memory space is updated to directly have mappings to IO devices as well.
This feature is called MMIO - Memory Mapped IO.
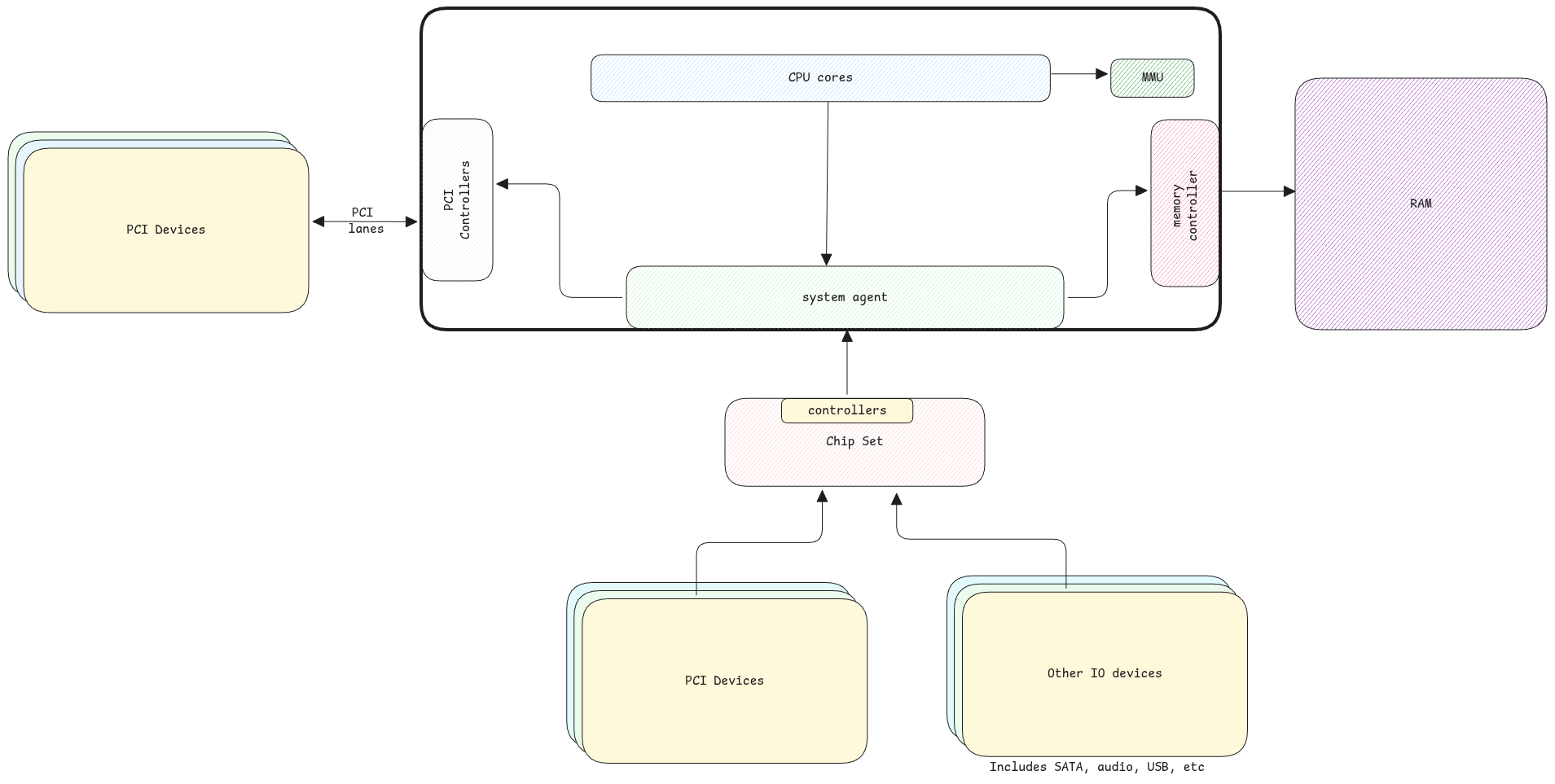
In case of MMIO, the registers of the devices are available in the CPU's memory space. Whereas in Port IO, the CPU has to specifically interact with the devices using separate instructions and addresses.
PIO is legacy. Not used anymore.
MMIO and PCI
MMIO is a technique that can work with or without PCI. So irrespective of whether the device supports PCI protocol, MMIO can work.
PCI - The physical addresses are allocated at boot by CPU and written to base address registers. non PCI - The address ranges are fixed in the device's firmware. MMU will map these physical addresses to virtual address space.