OAuth and OIDC
OIDC and OAuth are two terms that are often used interchangeably, hence it's important to understand the difference and build a clear mental model so that we don't forget the concepts.
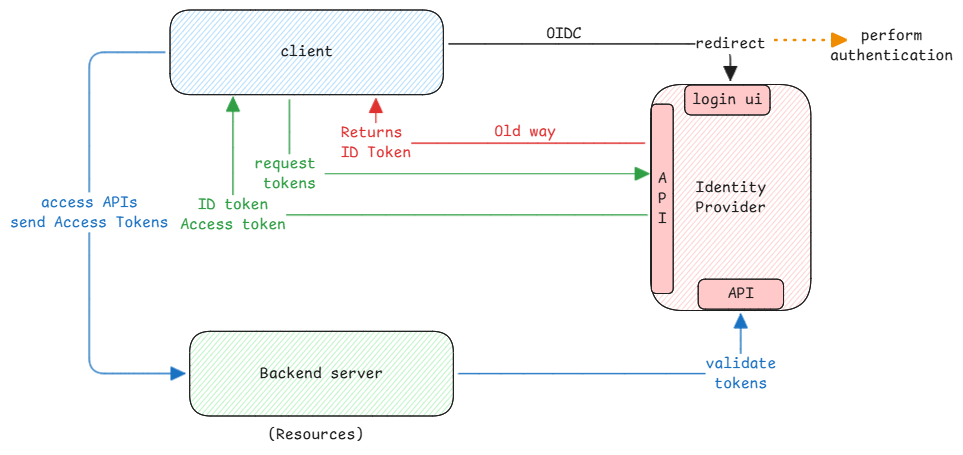
- OAuth - It's only about authorization. It's the concept where authorization to API resources are managed.
- OIDC - It's about authentication. It's comes about OAuth. Once the user is authenticated using OIDC
-
OIDC is about the authentication flow. After authentication it also emits the ID Token which contains user information. Additionally OIDC also brings in standards around API endpoints for identity providers.
-
OAuth is about authorizing access to resources without doing a regular login. Access tokens are issued by identity providers which is just another representation of user. This contains information about what resources the user can access.
OAuth existed first. OIDC was added on top using the standards which OAuth had already created.
It had already defined the flows that can be used to get access tokens from identity providers. OIDC just added the authentication layer on top of it and used it to get ID tokens.
It's very important to understand that both ID tokens and Access tokens are just base64 encoded strings. They're not encrypted.
But they're digitally signed with private keys. The clients only verify the signature using public keys to ensure that the tokens are valid.
Pure OIDC use cases
In case of LinkedIn using Google to login:
- Uses OIDC to authenticate the user using Google.
- Gets back an ID token from Google which contains user information.
- LinkedIn can use this information to map the user to it's user data.
- Then creates or uses it's own internal authorization mechanisms then to connect to it's APIs.
In this entire flow there is no OAuth used at all. Even though it receives access tokens, it never uses them to connect to any Google's services or connects to it's own APIs using them.